Product Description
Propeller Shaft Coupling Vibrator for Magnetic Bracelet Water Couplings Flexible Chain Fluid Flange Stainless Steel Spacer
Application of Propeller Shaft Coupling
A propeller shaft coupling is a mechanical device that connects 2 shafts together. It is used to transmit torque and rotation between the shafts. Propeller shaft couplings are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Marine. Propeller shaft couplings are used in marine applications to connect the engine to the propeller.
- Industrial. Propeller shaft couplings are used in industrial applications to connect different pieces of equipment together.
- Agricultural. Propeller shaft couplings are used in agricultural applications to connect the engine to the driveline.
- Off-highway. Propeller shaft couplings are used in off-highway applications to connect the engine to the driveline.
- Other. Propeller shaft couplings are used in a variety of other applications, such as wind turbines and conveyor belts.
There are a variety of different types of propeller shaft couplings, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The type of coupling that is best for a particular application will depend on the specific requirements of that application.
Here are some of the advantages of using propeller shaft couplings:
- They can transmit high torque and rotation.
- They are durable and can withstand a variety of harsh conditions.
- They are easy to install and maintain.
- They are available in a variety of sizes and styles to fit different applications.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using propeller shaft couplings:
- They can be expensive.
- They can be difficult to align properly.
- They can wear out over time.
Overall, propeller shaft couplings are a versatile and reliable way to connect 2 shafts together. They are used in a variety of applications and can be a valuable asset in any fleet.
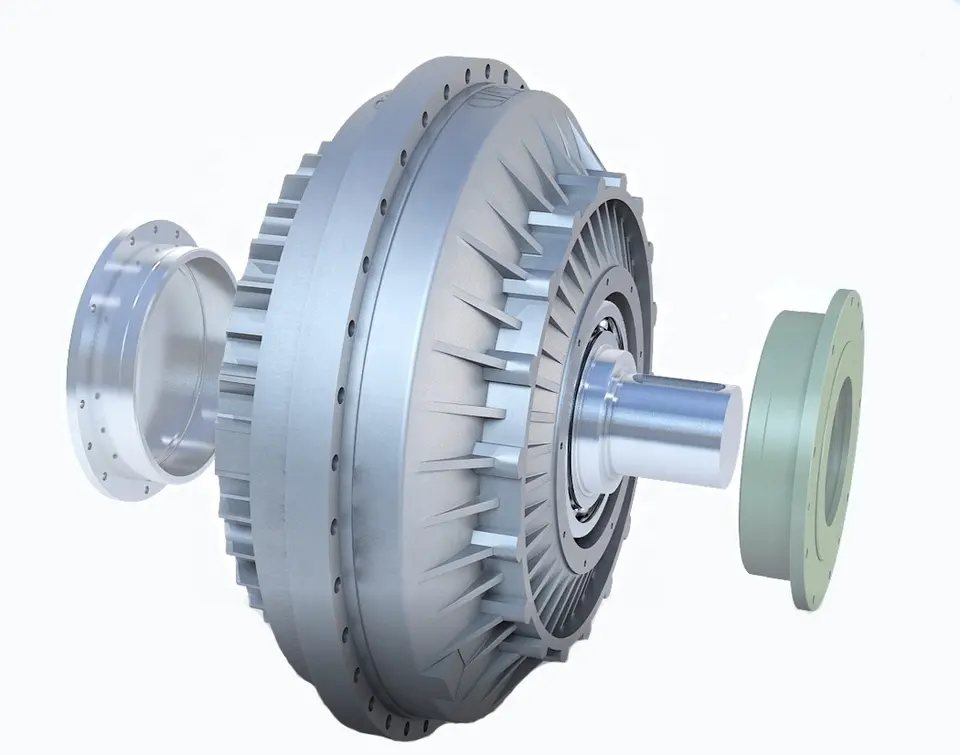
Noise and Vibration Issues with Fluid Couplings
Fluid couplings are generally designed to operate smoothly and quietly, but certain factors may lead to noise or vibration issues in some cases:
- Imbalanced Components: If the components of the fluid coupling, such as the impeller and runner, are not balanced properly, it can result in vibrations during operation. Regular maintenance and balancing can help mitigate this issue.
- High Operating Speeds: At high speeds, fluid couplings can generate more noise and vibration due to increased fluid turbulence. Using damping techniques or selecting appropriate coupling types can help reduce these effects.
- Fluid Level: Incorrect fluid levels in the coupling can lead to inadequate lubrication and cause noise during operation. Regularly checking and maintaining the fluid level can prevent such problems.
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the driving and driven shafts can result in increased noise and vibration. Proper alignment during installation is essential to avoid this issue.
- Fluid Characteristics: The choice of fluid can also impact noise and vibration levels. Using fluids with appropriate viscosity and lubricating properties can help achieve smoother and quieter operation.
- Aging or Contaminated Fluids: Over time, the fluid in the coupling may degrade or become contaminated, leading to increased friction and noise. Regular fluid replacement and maintenance can prevent this problem.
Addressing noise and vibration issues with fluid couplings involves proper installation, regular maintenance, and using high-quality components and fluids. Consulting with manufacturers or experts can help identify and resolve any specific noise or vibration concerns in the power transmission system.
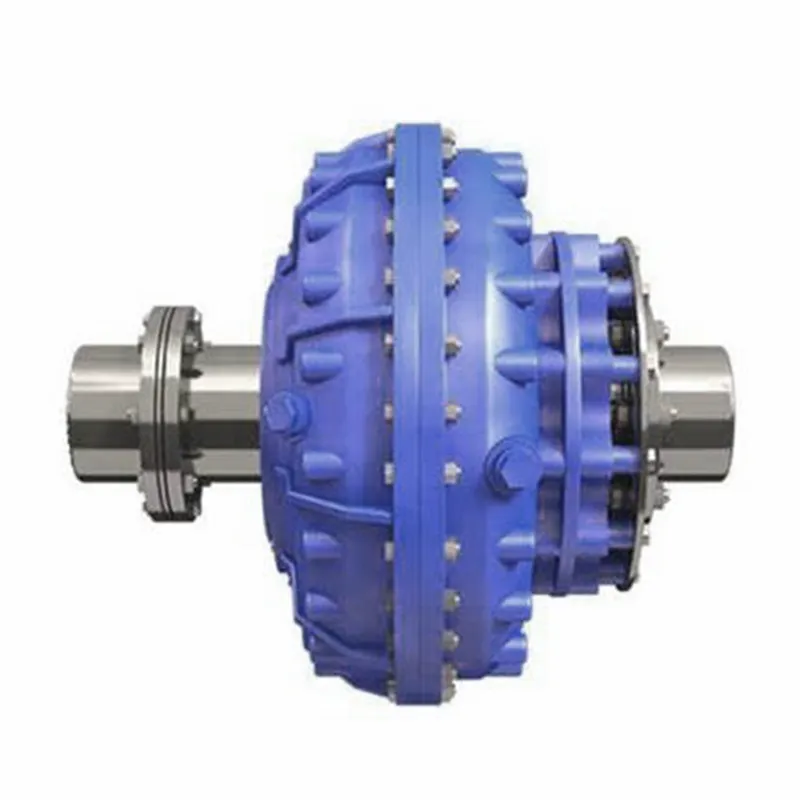

Fluid Coupling’s Handling of Load Changes during Operation
Fluid couplings are designed to efficiently handle changes in load conditions during operation, providing smooth and controlled power transmission. Here’s how fluid couplings accomplish this:
1. Torque Sensing: Fluid couplings are torque-sensitive devices. As the load on the driving side varies, the torque transmitted through the fluid coupling adjusts accordingly. When the load increases, the fluid coupling allows for some slip between the input and output sides, absorbing the excess torque. Conversely, when the load decreases, the fluid coupling reduces slip and transmits more torque, accommodating the new load conditions.
2. Load Distribution: In multi-drive systems, fluid couplings help to distribute the load evenly among connected equipment. When one machine experiences a higher load, the fluid coupling redistributes torque to prevent overloading of a specific component, ensuring a balanced power distribution.
3. Smooth Power Transmission: Fluid couplings offer a smooth and gradual transmission of power, even during load changes. Unlike mechanical clutches or direct couplings, fluid couplings provide a dampening effect, reducing shock loads and torsional vibrations when the load fluctuates. This minimizes stress on the connected machinery and enhances overall system reliability.
4. Soft Start and Stop: One of the significant advantages of fluid couplings is their ability to facilitate soft start and stop operations. During startup, the fluid coupling allows for controlled slip, gradually increasing the speed of the driven equipment. Similarly, during shutdown, the fluid coupling smoothly decelerates the connected machinery, preventing sudden stops that could cause damage or excessive wear.
5. Overload Protection: In situations where the load surpasses the rated capacity, the fluid coupling acts as an overload protector. By slipping and absorbing excess torque, it prevents damage to the connected equipment and the fluid coupling itself. This overload protection contributes to the safety and longevity of the entire system.
6. Automatic Adjustment: Fluid couplings automatically adjust to variations in load conditions without the need for manual intervention. This feature makes them suitable for applications with changing load demands, such as conveyors, crushers, pumps, and fans.
Overall, the ability of fluid couplings to handle changes in load conditions ensures stable and efficient power transmission while protecting the machinery from abrupt stress and wear. This makes fluid couplings an excellent choice for various industrial applications that require reliable and flexible power transfer.
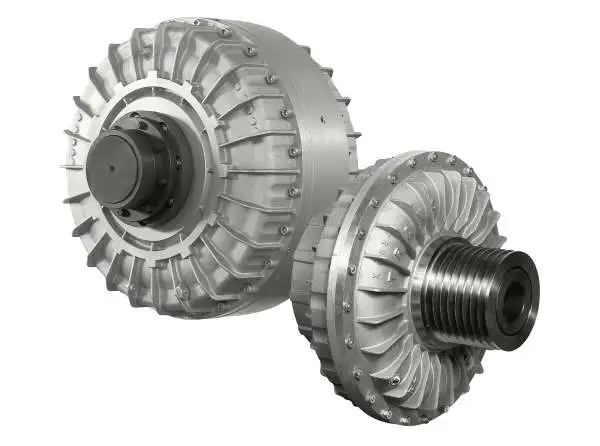

Comparison: Fluid Coupling vs. Torque Converter
Fluid couplings and torque converters are both hydrodynamic devices used in automotive and industrial applications to transmit power between an engine and a driven load. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences:
- Function: The primary function of both fluid couplings and torque converters is to transmit rotational power from the engine to the transmission or driven load. They allow for smooth power transmission and provide a degree of isolation between the engine and the load.
- Construction: Both devices consist of an impeller, a turbine, and a housing filled with hydraulic fluid (usually oil). The impeller is connected to the engine’s crankshaft, the turbine to the transmission/input shaft, and the housing is shared between the two.
- Torque Transmission: In a fluid coupling, the power is transmitted purely through hydrodynamic principles. The impeller accelerates the fluid, which then drives the turbine. However, there is no torque multiplication, and the output speed is always slightly less than the input speed. On the other hand, a torque converter can provide torque multiplication due to its stator, which redirects the fluid flow and increases the torque transmitted to the turbine.
- Lock-up Clutch: Some torque converters have a lock-up clutch that can mechanically connect the impeller and the turbine at higher speeds. This effectively eliminates the slip between the two elements and increases overall efficiency, similar to the operation of a fluid coupling at higher speeds.
- Automotive Use: Torque converters are commonly used in automatic transmissions in vehicles, while fluid couplings were more prevalent in older manual transmissions. However, modern manual transmissions generally use clutch systems instead of fluid couplings.
- Efficiency: Fluid couplings are generally more efficient than torque converters, especially at higher speeds. Torque converters can experience efficiency losses due to fluid slippage and the operation of the stator.
- Applications: Fluid couplings find applications in various industrial machinery, such as conveyors, pumps, and crushers, where the priority is smooth power transmission and overload protection. Torque converters are primarily used in vehicles, offering the benefit of automatic gear shifting and torque multiplication during acceleration.
Overall, both fluid couplings and torque converters play essential roles in power transmission, but their specific design and application characteristics determine their suitability for different use cases.


editor by CX 2023-08-30